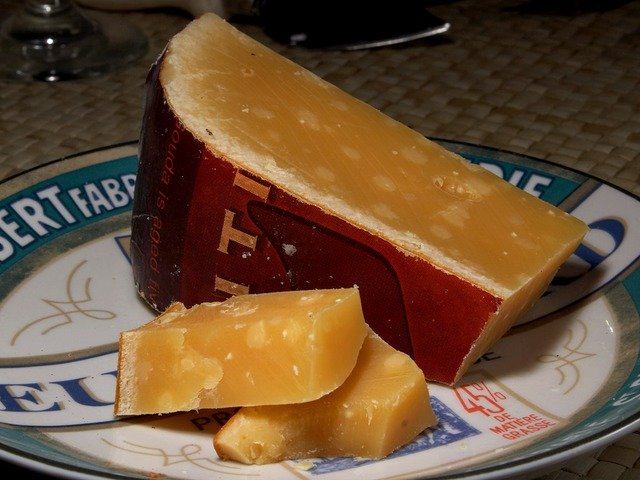
Gouda cheese is a semi-hard cheese that originated in the Netherlands, specifically in the city of Gouda Holland. The earliest records of Gouda date back to 1184, making it one of the oldest cheeses produced in the world. Gouda’s long history and continued popularity highlight its status as a versatile cheese enjoyed in many culinary applications.
What Makes Gouda Cheese Unique
Gouda cheese is typically made from pasteurized cow’s milk, though some artisans use goat’s milk or even raw milk to create distinct varieties. Smoked Gouda is another well-known type, offering a different flavour compared to the traditional version. The cheese-making process involves adding rennet to cultured milk, forming curd, and pressing it to achieve a smooth texture. Gouda’s moisture content and fat content vary depending on the milk used and how long the cheese ages, which directly influence its final texture and flavour. Like other cheeses, Gouda can be made in a range of styles to suit different tastes.
Herbs, seasonings, and nuts are sometimes added to the curd to enhance the flavour of Gouda. This cheese is known for its creamy texture and mild, sweet, and nutty flavour when young. As Gouda ages, it develops a firmer, crumbly texture, richer taste, and can even take on a caramel-like flavour with a slight crunchiness due to protein crystals.
Varieties and Characteristics
Gouda cheese comes in several varieties, mainly distinguished by how long the cheese is aged. Young Gouda, or Graskaas, is aged for about four weeks and is known for its high moisture content, smooth texture, and mild, sweet taste. Aged Gouda, on the other hand, is matured for more than 12 months, resulting in a harder cheese with a dense, crumbly texture and a more robust, nutty, and caramel-like flavour.
Smoked Gouda is another popular variation, where the cheese is smoked to add depth to its flavour. The wax rind of Gouda can be yellow, orange, or red for younger cheeses, while extra matured or aged Gouda often features a black wax covering.
Culinary Uses and Pairings
Gouda’s versatility makes it a favourite for cheese boards, cheese platters, and as a snack with crackers, fruits, and nuts. Its creamy and smooth texture means it melts well, making it suitable for sandwiches, burgers, soups, and sauces. In the Netherlands, Gouda is often used to enhance the flavour and aroma of dishes like soups and sauces.
Gouda cheese pairs well with wines such as Chenin Blanc or fruity Riesling. Its sweeter cheese profile also complements a variety of fruits and nuts, making it a staple on cheese boards and in salads.
Texture, Taste, and Aroma
The texture of Gouda cheese varies depending on its age. Young Gouda is soft, creamy, and mild, while aged Gouda is firmer, crumbly, and features a slight crunchiness. The taste of Gouda ranges from mild and sweet to rich, nutty, and caramel-like as the cheese matures. The aroma can be pungent, especially in aged varieties, but always retains a creamy and buttery undertone.
Conclusion
Gouda cheese stands out as a semi-hard, versatile cheese with a rich history and a wide range of flavours and textures. Whether enjoyed as a young, creamy cheese or as an aged, crumbly treat, Gouda brings a unique taste to cheese boards, recipes, and snacks around the world.
Looking to Learn More or Start Cheese Making?
We offer information and advice for cheese enthusiasts and those interested in cheese making. If you’re considering starting a cheese-making business or want to explore high-quality dairy processing equipment, we can provide guidance and recommend the best solutions for your needs.